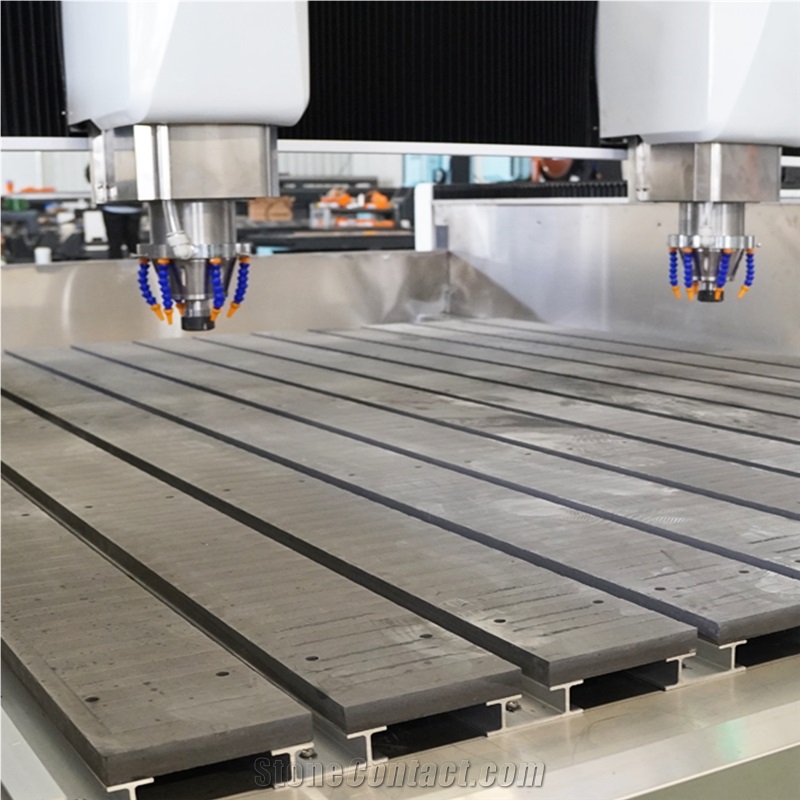
High-Production Duplex CNC Carving System
FOB Price:$8000-8200

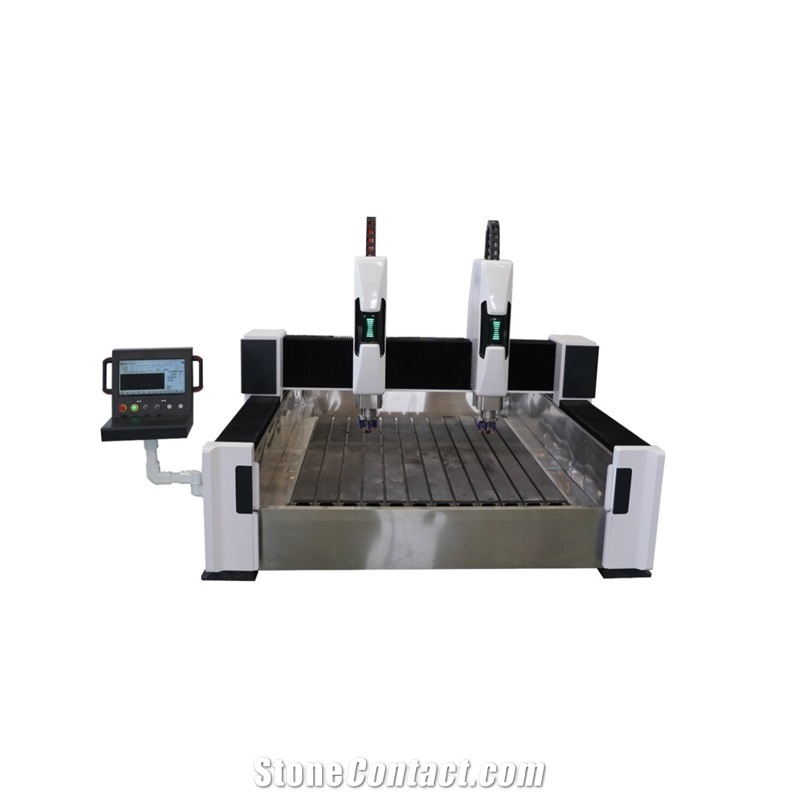
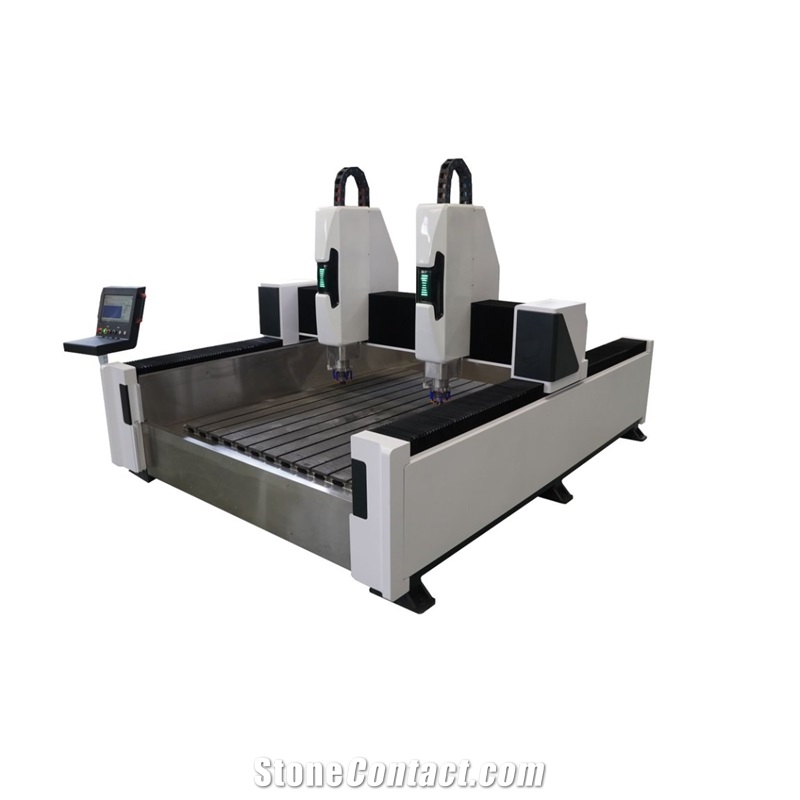
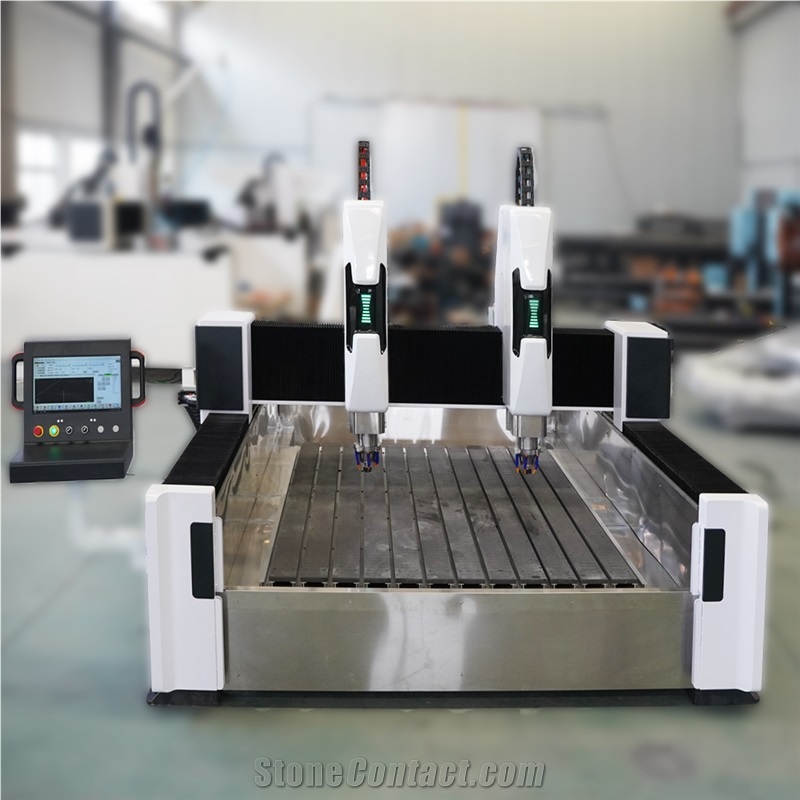
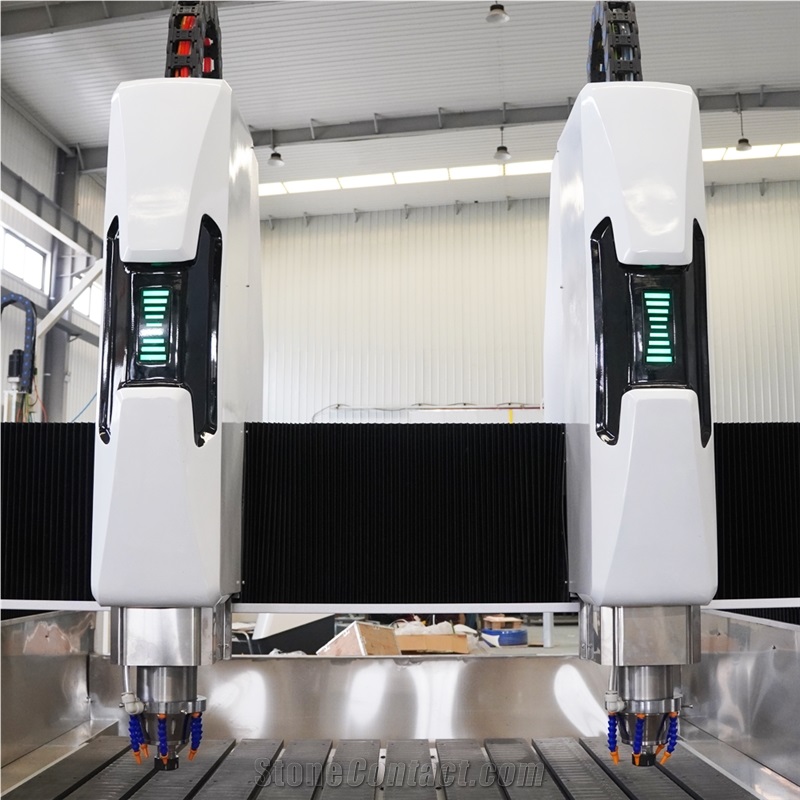
Functional Characteristics of Dual-Head Engraving Machines
A dual-head engraving machine is an efficient CNC device with two collaborative or independent engraving heads, widely used in woodworking, stone, metal, acrylic, and advertising fields. Its core features focus on efficiency, versatility, and precision:
I. Core Operation Modes
Independent Work: Two heads can use different tools/parameters to process the same or different workpieces simultaneously (e.g., one cutting contours, the other carving patterns), nearly doubling efficiency in batch production.
Collaborative Work: Heads cooperate on complex tasks, such as segmented engraving of large workpieces or rough/fine machining, reducing repositioning time.
II. Enhanced Efficiency
Batch Processing: Simultaneous processing of two workpieces shortens production cycles.
Reduced Auxiliary Time: Integrates multiple processes (e.g., drilling + engraving) to minimize clamping/tool change time.
III. Versatile Processing
Multi-Material Compatibility: Handles wood, stone, metal, acrylic, etc., with heads configurable for specific materials.
Multi-Task Support: Enables 2D/3D engraving, cutting, drilling, and milling—e.g., one head carves text, the other cuts contours in advertising production.
IV. Precision Control
High-Precision Components: Linear guides and servo motors ensure ±0.01mm positioning accuracy.
Synchronized Motion: Advanced CNC systems prevent offset in symmetric/cooperative patterns.
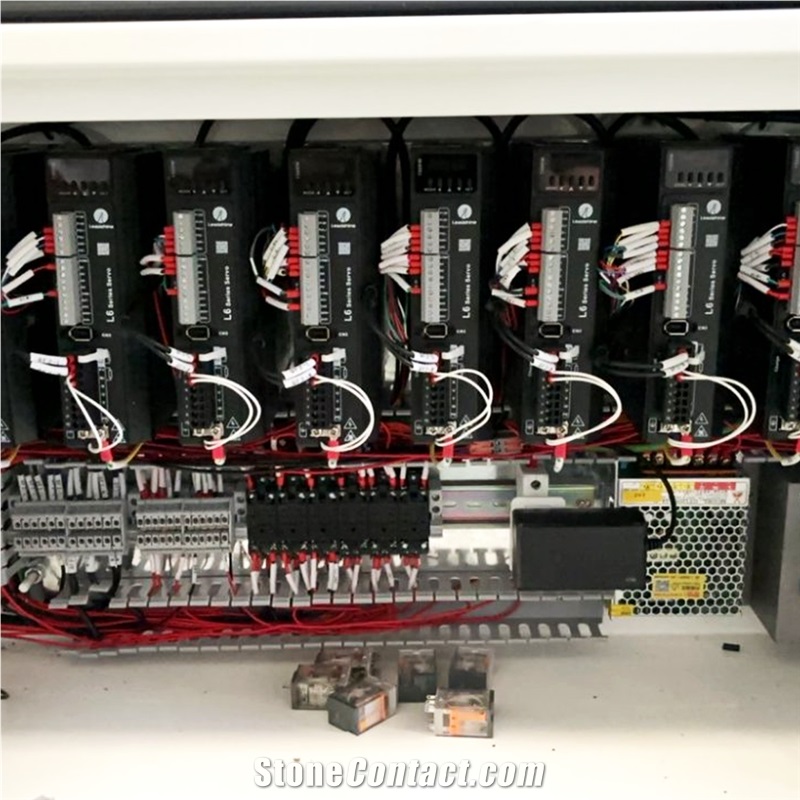
V. Intelligent & Reliable
User-Friendly Interface: Easy parameter setting and task simulation to avoid collisions.
Safety Features: Overload protection, emergency stop, and tool breakage detection ensure stability.
Ideal for boosting productivity and expanding capabilities in diverse manufacturing sectors.
Parameters |
Unit |
IK-2513 |
Main spindle motor power |
kw |
7.5 |
Max. processing length |
mm |
2500 |
Control System |
NC.studio |
|
Main spindle speed |
r/min |
6000-24000 |
Total power |
kw |
21 |
Max. Processing Width |
mm |
1300 |
Machine overall width |
mm |
2800 |
Approx. Weight |
T |
3.6 |
Work table dim.(LxWxH) |
mm |
2500*1300 |
Machine overall length |
mm |
4300 |
NC Studio is a computer numerical control system primarily used to control various processing equipment, such as milling machines, lathes, laser cutting machines, and stone cutting-grinding all-in-one machines. Its working principle is based on computer technology, automatic control theory, and communication technology, aiming to convert digital processing instructions into actual actions of the equipment to achieve precise processing operations. The details are as follows:
Instruction Input and Parsing:
Multiple Input Methods: Operators can manually input processing instructions through the operation interface of NC Studio, or import G-code files generated by CAD/CAM software (such as UG, Mastercam, AutoCAD, etc.). These G-codes are a universal numerical control programming language that specifies key processing parameters in detail, including tool path, cutting speed, and feed rate.
Instruction Parsing Process: After the system reads the input instructions, its core processor decodes and calculates these instructions. For example, it parses coordinate values and motion instructions (such as linear interpolation G01, circular interpolation G02, etc.) in the G-code into specific motion information of each axis (X, Y, Z axes, etc.) of the equipment, clarifying the movement direction, distance, and speed of each axis.
Motion Control:
Role of Motion Control Card: NC Studio relies on a motion control card to achieve precise control of equipment movement. Based on the parsed instructions, the motion control card calculates the motion trajectory and real-time position of each axis, and generates corresponding pulse signals or analog signals.
Operation of Driving Motor: These signals are transmitted to the servo driver or stepper driver, which drives the servo motor or stepper motor to operate according to the received signals. The motor drives components such as the workbench and tools of the equipment through mechanical transmission devices (such as ball screws, timing belts, etc.), thereby realizing the precise positioning of the tool relative to the workpiece and completing various complex processing paths such as straight lines, curves, and arcs. For example, when the stone cutting-grinding all-in-one machine performs cutting operations, the motion control card can accurately control the cutting tool to move along the preset stone cutting path.
Tool Path Planning and Optimization:
Path Planning Strategies: For complex processing graphics, NC Studio automatically performs tool path planning. For instance, it adopts different strategies such as contour parallel machining, spiral machining, and parallel line machining to ensure that the tool can cut the workpiece efficiently and accurately while minimizing empty strokes and tool wear. When edging the stone cutting-grinding all-in-one machine, the system plans the movement path of the grinding tool according to the set edging shape (such as right-angle edge, bevel edge, rounded edge, etc.).
Optimization Function: The system also has a path optimization function, which can check and adjust the generated tool path. Through optimization, problems such as interference and collision in the tool path can be avoided, and processing efficiency can be improved. For example, under the premise of ensuring processing quality, the cutting speed and feed rate are reasonably adjusted to reduce processing time.
Real-Time Monitoring and Feedback:
Monitoring Equipment Status: NC Studio monitors the operating status of the equipment in real-time, including the rotational speed and load of the motor, the position feedback of each axis, the current position of the tool, etc. For example, the rotation angle of the motor is fed back in real-time through the encoder connected to the motor, so as to accurately calculate the actual displacement of the workbench.
Feedback Adjustment Mechanism: When the system detects a deviation between the actual motion state and the instruction requirements, it will automatically adjust. For example, if it is found that the actual position of a certain axis deviates from the target position, the motion control card will timely adjust the output signal according to the feedback information to correct the motion of the motor, ensuring processing accuracy. In addition, if the equipment has abnormal conditions (such as overload, overtravel, etc.), the system will immediately issue an alarm and take corresponding protective measures, such as stopping the operation of the equipment, to prevent equipment damage and processing accidents.
Auxiliary Function Control:
Support for Multiple Auxiliary Functions: In addition to the core motion control function, NC Studio is also responsible for controlling various auxiliary functions of the equipment. For example, when the stone cutting-grinding all-in-one machine is working, the system will control the cooling system (such as a water pump) to turn on to cool the tools and stones during cutting or edging, preventing overheating and wear of the tools and thermal deformation of the stones; at the same time, it will control the dust suction device to work to timely absorb the dust generated during processing and keep the working environment clean.
Coordinated Operation of Functions: These auxiliary functions cooperate with the processing operation of the equipment, and are uniformly scheduled by NC Studio according to the processing technology requirements and equipment operating status to ensure the smooth progress of the entire processing process and improve processing quality and equipment
Stone engraving machines use CNC systems to turn digital designs into stone carvings via coordinated tool movement.
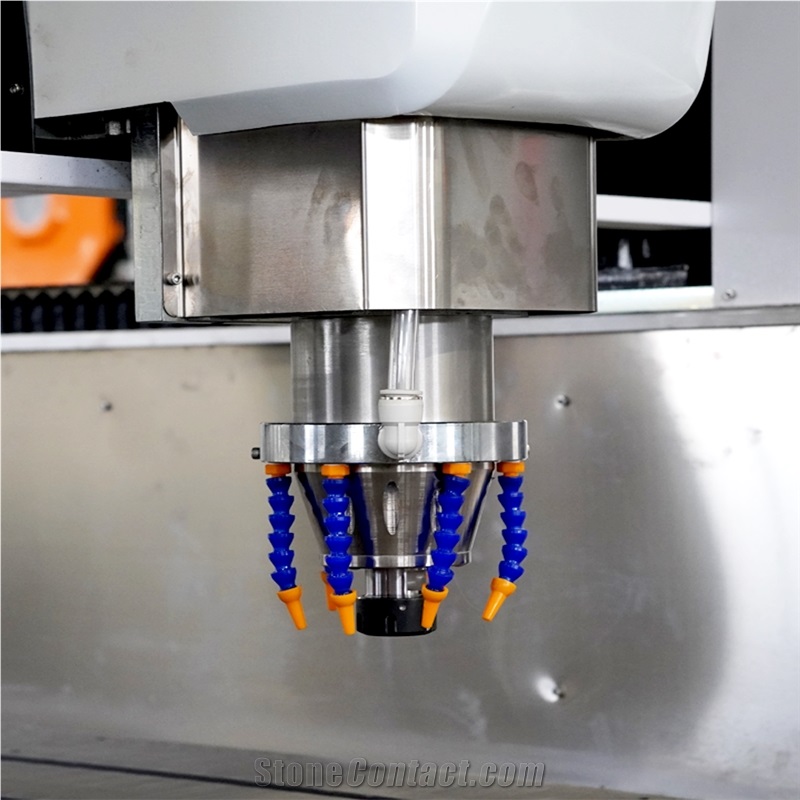
They take G-code instructions (from CAD/CAM software) and convert them into signals for axis movement (X, Y, Z, and rotary A for 3D work). A high-speed spindle with diamond or carbide tools grinds the stone, adjusting speed and pressure based on stone hardness.
Axes work together: X/Y trace patterns, Z controls depth, and A rotates stone for curves. Sensors monitor tool position and stone stability, correcting deviations in real-time.
Cooling and dust removal systems run alongside, while advanced models auto-change tools for relief, line, or 3D carving. This setup ensures precise, efficient stone engraving.
4 / 5 Very satisfied
Hei*** 
9/19/2025 2:40:16 AM
Related Products:

JINAN IKCNC TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD

 China
China
 1YR
1YR

Tel:86-15615410983
Contact supplier